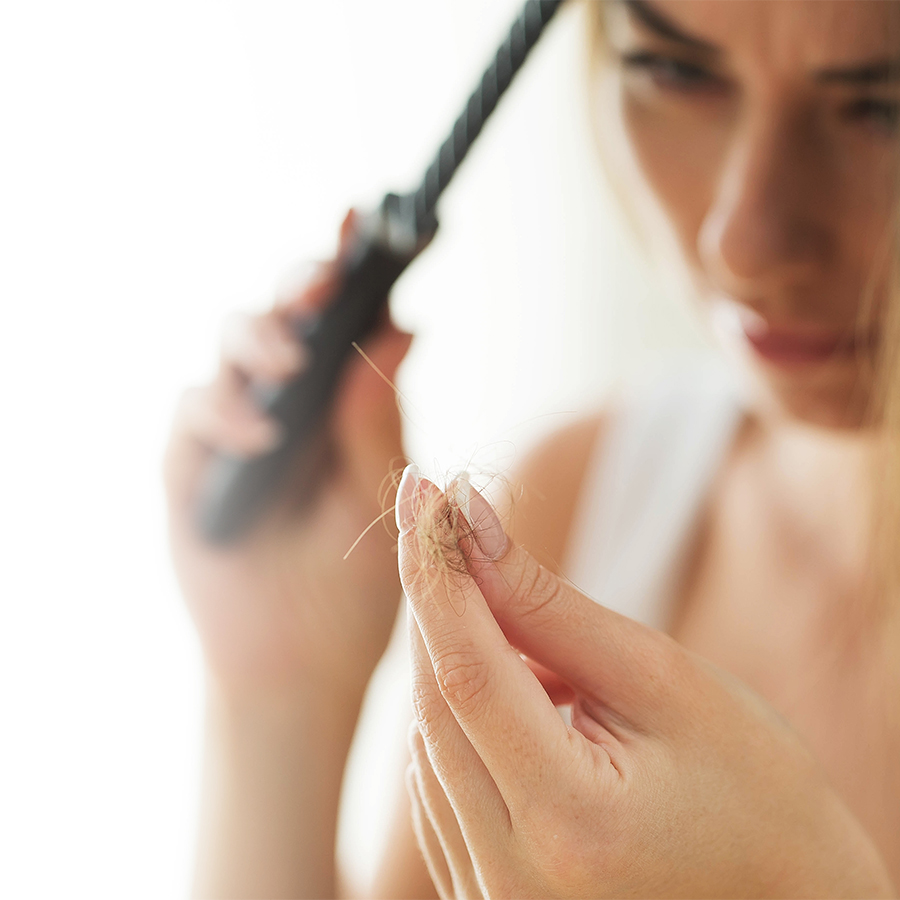
Have you noticed an unusual increase in the number of hairs on your brush or in your shower? Hair loss can be a cause for concern, but it is important to know that this is not always synonymous with a serious problem. Understanding the mechanisms of hair loss and identifying its causes will help you to deal with it more effectively and choose the right treatment.
What causes hair loss?
First and foremost, it is essential to understand that hair loss is a completely normal and natural phenomenon that is simply part of the hair’s life cycle. Distinguishing between normal hair loss and problem hair loss is essential in order to know when to take action. The hair cycle consists of three stages.
The natural life cycle of hair
- The anagen stage, or active growth stage, lasts between two and six years. During this period, around 85% of your hair grows continuously from its follicle.
- The next stage is called catagen. This is a transitional period lasting around two weeks, during which growth gradually slows to a standstill.
- Finally, the telogen stage corresponds to the resting stage, which lasts around three months. During this stage, 10 to 15% of hairs remain attached to the root without growing, until they fall out naturally to make way for new hairs from the same follicles.
Once this natural cycle is completed and the hair has fallen out, new hair grows from the same roots. However, the hair growth cycle can be influenced to a greater or lesser extent by certain factors, such as age, heredity, hormones, illness, or medical treatments, which can lead to abnormal hair loss.
How much hair do we lose each day?
According to Health Canada, it is completely normal to lose between 50 and 100 hairs per day as part of the natural hair cycle. Beyond this threshold, abnormal hair loss may require special attention. In all cases, it is recommended to seek advice from a healthcare professional.
When should you worry about hair loss?
Certain signs should prompt you to consult a healthcare professional without delay
- If you lose more than 100 hairs per day on a prolonged basis.
- If you notice visible thinning on the scalp or bald spots.
- Sudden, massive hair loss accompanied by intense itching, redness, bald patches, or flaking of the scalp. This may indicate a dermatological condition requiring medical treatment.
Other cases can also raise red flags. Like hair loss that occurs after a change in medication, that is accompanied by intense fatigue, unexplained weight gain or loss, or that also affects eyebrows and eyelashes, also merits medical consultation. These symptoms may reveal a hormonal imbalance, a significant nutritional deficiency or an underlying autoimmune disease.
Warning! In women, sudden hair loss accompanied by irregular periods, acne or excessive hair growth may signal polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). In both men and women, hair loss associated with sensitivity to cold, dry skin or constipation may indicate a thyroid disorder..
What causes hair loss?
Hair loss is the result of multiple factors that vary according to gender, age and general state of health. Identifying the cause allows you to choose the most appropriate treatment.
➤ Hormonal causes in women
Hormonal fluctuations represent one of the main causes of hair loss, particularly in women. During pregnancy, an increase in estrogen prolongs the hair growth stage, resulting in denser hair.
However, after giving birth, the sudden drop in these hormones causes significant hair loss, known as postpartum telogen effluvium, which affects up to 50% of new mothers, according to the Canadian Dermatology Association. While impressive, this drop is temporary and usually resolves within six months after giving birth.
Menopause is another critical period for women’s hair health. The decrease in estrogen and the relative increase in androgens can trigger androgenetic alopecia in women, characterized by diffuse thinning on the top of the head.
➤ Androgenetic alopecia in men and women
Hair loss in men most often manifests as androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male pattern baldness. This progressive hereditary condition affects approximately 70% of men during their lifetime.
Although it mainly affects men, around 40% of women will experience some form of alopecia before the age of 50. In women, hair loss manifests itself differently, with diffuse thinning over the entire scalp rather than localized baldness.
➤ Stress and environmental factors
Chronic stress is a major trigger for reactive hair loss, which is particularly common in women.
- An intense emotional shock;
- A prolonged period of overwork;
- Psychological trauma;
These three situations can lead to hair loss, even two to three months after the triggering event.
Seasonal changes also influence the hair cycle. Particularly in autumn and spring, when the scalp adapts to variations in temperature and light. This seasonal drop, although normal, can be accentuated by other stress factors.
Be careful, aggressive hair treatments such as repeated colouring, chemical straightening, excessive use of heated styling tools or tight hairstyles (braids, tight buns, extensions) weaken the hair fibre and can cause traction alopecia.
➤ Medical and medicinal causes
Some autoimmune diseases, such as alopecia (alopecia areata), cause localized hair loss in patches, resulting from an immune system attack on the hair follicles.
Many medications can also cause hair loss due to their side effects.
- Cancer treatments (chemotherapy);
- Anticoagulants;
- Certain antidepressants;
- Blood pressure medication;
- Acne medications containing vitamin A (retinoids);
- Certain hormone treatments.
What deficiencies can cause hair loss?
Nutritional deficiencies play a crucial role in hair health. Several deficiencies can weaken hair and accelerate hair loss.
✚ Iron deficiency and anemia
Iron deficiency is the nutritional deficiency most frequently associated with hair loss, particularly in women of childbearing age. Iron plays an essential role in the production of hemoglobin, which transports oxygen to cells, including hair follicles.
Did you know? According to Health Canada, adult women need 18 mg of iron a day before menopause, compared with 8 mg for adult men. This difference can be explained by women's monthly menstrual losses.
✚ Group B vitamin deficiencies
B vitamins, particularly biotin (vitamin B7), niacin (vitamin B3), cobalamin (vitamin B12) and folic acid (vitamin B9), are essential for hair growth and health. Vitamin B12, found mainly in animal products, is essential for the formation of red blood cells and oxygenation of hair follicles.
✚ Zinc and proteins
Zinc is involved in cell growth, tissue repair and the maintenance of sebaceous glands surrounding hair follicles. Zinc deficiency weakens hair, slows growth and can even alter its texture. Proteins make up the very structure of hair, 95% of which is keratin, a fibrous protein.
✚ Vitamin D and essential fatty acids
Vitamin D plays a role in the creation of new hair follicles and the regulation of the hair cycle. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in oily fish, flaxseed and walnuts, nourish the hair, promote thickening and reduce scalp inflammation.
How to stop or slow down hair loss?
Whether reactive or chronic, it is important to take action from the very first signs of hair loss. A good shampoo and a gentle treatment suitable for hair loss is the right way to go.
However, if you know you are affected by reactive hair loss, certain over-the-counter products are specially designed to rebalance the scalp, strengthen the hair, and stimulate the roots.
Conversely, if your hair loss is chronic, use an anti-hair loss shampoo that tones the scalp while strengthening the hair. Formulated with a thickening treatment that stimulates new hair growth and protects existing hair, you will create the ideal environment to combat hair loss.
How to regrow hair?
Three essential habits are required to promote hair regrowth:
• Targeted treatments
Recognized drug treatments such as minoxidil, available over the counter as a lotion or foam, stimulate blood circulation in the scalp and prolong the hair growth phase, with visible results after three to four months of regular use.
• Proper nutrition
Make sure you get enough protein (meat, fish, eggs, legumes), iron (red meat, spinach, lentils), zinc (oysters, nuts, seeds) and vitamins B, D and omega-3, as deficiencies in these essential nutrients considerably slow hair growth.
• Proper treatments
Fortifying shampoos and serums enriched with biotin, caffeine, copper peptides and B vitamins nourish hair follicles and create a favourable environment for regrowth. The power of plant-based ingredients is also effective against hair loss as well as hair regrowth.
Quick tips for better regrowth:
- Massage your scalp daily for two to three minutes to stimulate microcirculation.
- Manage stress with relaxation techniques.
- Sleep at least 7 to 8 hours a night.
- Avoid aggressive treatments, such as frequent colouring, heated tools and tight hairstyles that weaken the hair.
Your Jean Coutu pharmacist can guide you to the products best suited to your type of hair loss, and refer you to a doctor if your situation requires a prescription for stronger treatments. Ask your cosmetician for advice.